Ultraviolet light is responsible for summer tans and sunburns. However, too much exposure to UV radiation is damaging to the living tissue.
Ultraviolet light is not detectable by the human eye. But there are some insects that are able to see the ultraviolet light. Our bodies use ultraviolet light to make vitamin D. If the ultraviolet light exposure is too much then it can be very harmful as it can cause cancer.
When Ultraviolet light descends on certain materials, ultraviolet light may cause them to fluoresce. It emits electromagnetic radiations of lower energy such as visible light.
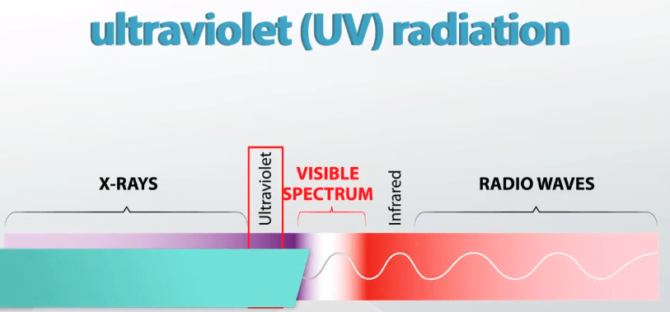
The range of ultraviolet light:
Ultraviolet radiation lies between wavelengths of about 400 nanometers (1 nanometer [nm] is 10−9metre) on the visible-light side and about 10 nm on the X-ray side, though some authorities extend the short-wavelength limit to 4 nm.
Regions in which ultraviolet light is divided:
An ultraviolet radiation is commonly divided into four regions:
- near (400–300 nm)
- middle (300–200 nm)
- far (200–100 nm)
- extreme (below 100 nm)
Divisions of ultraviolet light:
Based on the interaction of wavelengths of ultraviolet radiation with biological materials, three divisions have been designated:
- UVA (400–315 nm): It is also called black light.
- UVB (315–280 nm): It is responsible for the radiation’s best-known effects on organisms.
- UVC (280–100 nm): It does not reach earth’s surface.
How ultraviolet light is produced?
Ultraviolet radiation is produced by high-temperature surfaces, such as the Sun.
It is produced in a continuous spectrum and by atomic excitation in a gaseous discharge tube as a discrete spectrum of wavelengths.
Most of the ultraviolet radiation in sunlight is absorbed by oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere, which forms the ozone layer of the lower stratosphere. Of the ultraviolet that does reach Earth’s surface, almost 99 percent is UVA radiation.
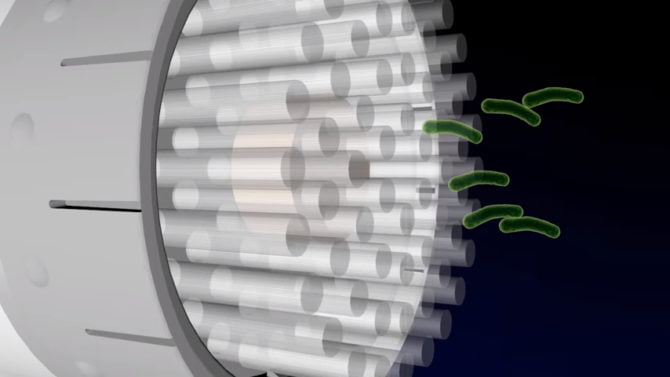
An ultraviolet UV lamp:
An ultraviolet UV lamp has been developed that basically kills the influenza virus. A study has shown that it is not injurious to human eyes, skin, and health.

Objective:
The objective of this technology is to intercept the outspread of seasonal flu in public places such as schools, hospitals, restaurants, libraries, offices, park, stores etc. An ultraviolet light is especially effective and efficient in killing germs, microbes, bacteria, and viruses.
UV devices:
There are UV devices that have been used for sterilization and for the medical equipment in the hospitals.
But the conventional germicidal lamp is not safe for the humans when they are around.
UV light can effectively kill airborne influenza:
UV light can effectively kill airborne influenza. It can kill bacteria without harming the human tissues. A study has shown that broad-spectrum germicidal UV light that has a wavelength between 200 to 400 nanometers is extremely active and efficient in killing bacteria, microbes, and viruses by spoiling the molecular bonds that hold the DNA together.
This conventional UV light is used to sterilize the medical equipment. The conventional germicidal UV is also harmful to human health. It can cause skin cancer.
Brenner and his colleagues hypothesized that a narrow spectrum of ultraviolet light called far-UVC could destroy microbes without damaging healthy tissue.
UVC light has the very limited range and it cannot go through the outer dead cell layer of human skin or the tear layer in the eye. However, it is not harmful to human health.
Also read: All you need to know about fast-acting depression spray
Conclusion:
Ultra-violet rays can provide numerous benefits of sterilization i.e. the removal of microbes and viruses from the equipment. It can definitely reduce the transmission of illnesses caused by them. There is special stress on the transmission of influenza virus but practical use of ultraviolet rays is beyond the removal of these viruses.

